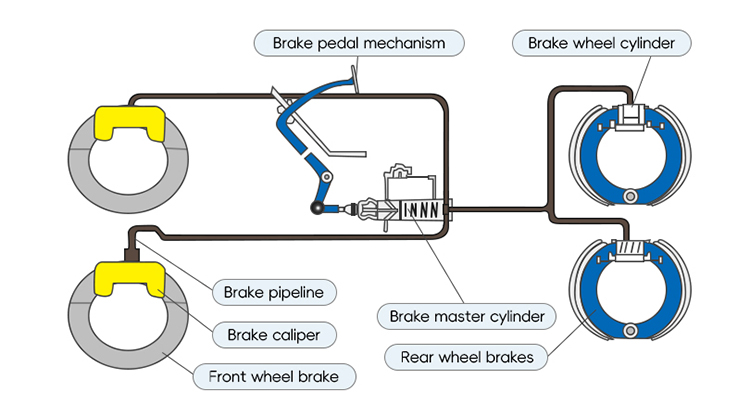
Brake systems are crucial for the safe operation of vehicles, and two important components that work together to ensure effective braking are the brake master cylinder and the brake wheel cylinder. In this blog post, we will explore the connection between these two components and their roles in the braking system.
The brake master cylinder is responsible for generating hydraulic pressure in the brake system. When the driver applies the brake pedal, the master cylinder converts the mechanical force into hydraulic pressure. This pressure is then transmitted through the brake lines to the brake wheel cylinders.


The brake wheel cylinders are located at each wheel of the vehicle. They are responsible for applying force to the brake shoes or brake pads, which in turn press against the brake drums or brake rotors to create friction and slow down or stop the vehicle. The brake wheel cylinders receive hydraulic pressure from the brake master cylinder, causing them to expand and push the brake shoes or pads against the drums or rotors.


The connection between the brake master cylinder and the brake wheel cylinders is established through the brake lines. These lines carry the hydraulic fluid, which carries the pressure generated by the master cylinder, from the master cylinder to the wheel cylinders. The hydraulic fluid transfers the force from the master cylinder to the wheel cylinders, enabling the braking action at each wheel.
It is important to note that the brake master cylinder and the brake wheel cylinders are both vital components that require regular maintenance and inspection. Any leaks, damage, or malfunction in either of these components can compromise the braking system's performance and safety. Proper maintenance and prompt repairs are essential to ensure the effectiveness of the brake system.
In conclusion, the brake master cylinder and the brake wheel cylinders work in tandem to ensure reliable and efficient braking. The master cylinder generates hydraulic pressure, which is transmitted through the brake lines to the wheel cylinders. The wheel cylinders then apply force to the brake shoes or pads, creating the necessary friction to slow down or stop the vehicle. Understanding the connection between these components highlights the importance of proper maintenance and care for a safe and functional braking system.